- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
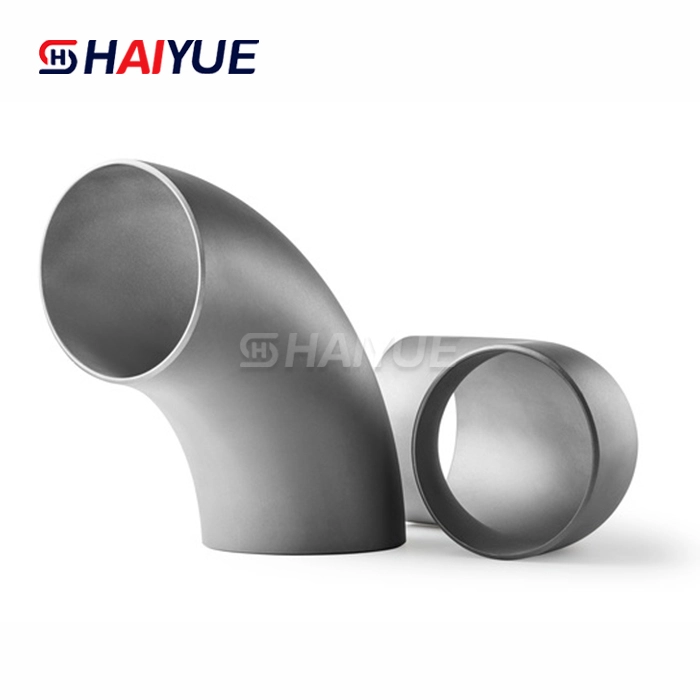
Pure Titanium Pipes: Strength and Reliability in Heavy Industries
When it comes to heavy industries, the choice of materials can make or break a project. Among the various options available, pure titanium pipes have emerged as a game-changer, offering unparalleled strength and reliability. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the world of pure titanium pipes and their significant impact on industrial applications.

The Remarkable Properties of Pure Titanium Pipes
Pure titanium pipes are not just another option in the world of industrial materials; they're a revolution in themselves. These pipes boast an impressive array of properties that make them stand out in even the most demanding environments.
First and foremost, the strength-to-weight ratio of pure titanium is simply astounding. Despite being incredibly strong, titanium pipes are surprisingly lightweight. This unique combination allows for the construction of robust systems without the burden of excessive weight, a factor that's particularly crucial in aerospace and marine applications.
But the benefits don't stop there. Pure titanium pipes are also known for their exceptional corrosion resistance. Unlike many other metals, titanium forms a protective oxide layer when exposed to air or water. This natural shield makes pure titanium pipes highly resistant to various forms of corrosion, including pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking.
Temperature Resistance and Durability
Another feather in the cap of pure titanium pipes is their impressive temperature resistance. These pipes maintain their structural integrity across a wide range of temperatures, from the freezing cold to scorching heat. This property makes them invaluable in industries where extreme temperature fluctuations are the norm, such as chemical processing and power generation.
The durability of pure titanium pipes is also worth noting. They have an incredibly long lifespan, often outlasting many other materials used in similar applications. This longevity translates to reduced maintenance costs and fewer replacements, making pure titanium pipes a cost-effective choice in the long run.
Applications of Pure Titanium Pipes in Heavy Industries
The unique properties of pure titanium pipes have paved the way for their use in a wide range of heavy industries. Let's explore some of the key sectors where these remarkable pipes are making a significant impact.
Chemical Processing and Petrochemicals
In the chemical processing industry, pure titanium pipes are a first choice for handling corrosive substances. Their resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including chlorine, sulfuric acid, and various salts, makes them ideal for transporting aggressive fluids. In petrochemical plants, these pipes are often used in heat exchangers and distillation columns, where their corrosion resistance and heat transfer properties shine.
Offshore Oil and Gas
The harsh marine environment of offshore oil and gas operations is no match for pure titanium pipes. Their excellent resistance to seawater corrosion, combined with their high strength and light weight, makes them perfect for subsea applications. From risers to flowlines, pure titanium pipes are helping to extend the life of offshore installations and reduce maintenance costs.
Power Generation
In power plants, particularly those utilizing seawater for cooling, pure titanium pipes play a crucial role. Their ability to withstand both high temperatures and corrosive environments makes them ideal for condenser tubing and heat exchangers. The use of pure titanium pipes in these applications has led to increased efficiency and reduced downtime in power generation facilities worldwide.
The Future of Pure Titanium Pipes in Industry
As we look to the future, the role of pure titanium pipes in heavy industries is set to grow even further. With increasing demands for efficiency, durability, and environmental sustainability, these remarkable pipes are positioned to meet the challenges head-on.
Advancements in Manufacturing
Ongoing advancements in manufacturing techniques are making pure titanium pipes more accessible and cost-effective. Improved welding methods, such as friction stir welding, are enhancing the joining capabilities of titanium pipes, opening up new possibilities for their use in complex systems.
Additionally, the development of new titanium alloys is expanding the range of properties available, allowing for even more specialized applications. These innovations are not only improving the performance of pure titanium pipes but also making them a viable option for a broader range of industries.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
In an era where sustainability is paramount, pure titanium pipes are gaining attention for their eco-friendly characteristics. Their long lifespan and recyclability contribute to reduced waste and resource consumption. Moreover, the energy efficiency gains in processes using titanium pipes can lead to a smaller carbon footprint for industrial operations.
The corrosion resistance of pure titanium pipes also plays a role in environmental protection. By preventing leaks and spills of potentially harmful substances, these pipes help maintain the integrity of industrial systems and protect surrounding ecosystems.
Emerging Markets and Applications
As industries continue to evolve, new applications for pure titanium pipes are emerging. In the field of renewable energy, for instance, these pipes are finding use in geothermal power plants and offshore wind farms. The aerospace industry, always on the lookout for lightweight and strong materials, is also increasing its utilization of pure titanium pipes in various aircraft systems.
The medical industry, too, is exploring the potential of pure titanium pipes. Their biocompatibility and corrosion resistance make them excellent candidates for use in medical devices and implants, opening up a whole new realm of possibilities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pure titanium pipes represent a pinnacle of material science in heavy industries. Their unique combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties makes them an invaluable asset in a wide range of applications. As we continue to push the boundaries of industrial capabilities, pure titanium pipes will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of heavy industries. If you want to know more about titanium products, please contact us: Jolina@bjhyti.com.
References
1. Lutjering, G., & Williams, J. C. (2007). Titanium (2nd ed.). Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
2. Boyer, R., Welsch, G., & Collings, E. W. (1994). Materials Properties Handbook: Titanium Alloys. ASM International.
3. Donachie, M. J. (2000). Titanium: A Technical Guide (2nd ed.). ASM International.
4. Peters, M., Hemptenmacher, J., Kumpfert, J., & Leyens, C. (2003). Titanium and Titanium Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications. Wiley-VCH.
5. Schutz, R. W., & Thomas, D. E. (1987). Corrosion of Titanium and Titanium Alloys. ASM Handbook, Volume 13: Corrosion. ASM International.
Main Products
Applied Industries
Be used in a wide range of industries.

Electrolytic copper foil manufacturing industry

Hydrometallurgy industry

Sewage treatment industry

Cyclone electrolysis industry

Etching liquid electrolysis recovery industry

Electrolytic sodium hypochlorite industry
Learn about our latest products and discounts through SMS or email